의료법인 유투의료재단 신축공사
-
Location
열분해
-
Client
의료법인 유투의료재단
-
용도
1종 근린생활시설1종
-
규모
지하3층~지상7층 / 7,917.81㎡
-
공사기간
2025.02 ~ 2026.12

We provide innovative, eco-friendly wastewater solutions based on global licenses, diverse treatment methods, sludge reduction, and biogas recovery, supporting ESG goals.
Global License-Based Solutions


Global License-Based Solutions
Providing Proprietary Environmental Solutions Under Official PAQUES Licensing
Wide Range of Wastewater Treatment Technologies


Wide Range of Wastewater Treatment Technologies
Including Anaerobic, Aerobic, Membrane Filtration, Adsorption, Oxidation, and More
Sludge Reduction & Biogas Resource Recovery


Sludge Reduction & Biogas Resource Recovery
Achieving Sludge Volume Reduction and Biogas Production for Energy Resource Utilization
ESG-Based Environmental Solutions


ESG-Based Environmental Solutions
Providing Sustainable ESG-Based Environmental Solutions
Reactor Type
| Equipment |
IC Reactor 
Economical wastewater treatment equipment that removes COD by using anaerobic microorganism, and can recover methane generated in this process to use it as an energy source |
ICX 
It is the latest technology developed based on the experience of UASB and IC Reactor, and it is possible to convert not only new wastewater treatment equipment but also anaerobic wastewater treatment equipment, which has operational problems such as microbial loss, to ICX |
UASB Plus 
It is the technology that improved the disadvantages of UASB, and it is possible to convert existing tanks that are not in use and to improve wastewater treatment facilities with small initial cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| Advantage |
|
|
|
| Applicable range |
(COD concentration x flow rate) : 20~30kg COD/㎥day |
(COD concentration x flow rate) : 30~60kg COD/㎥day |
(COD concentration x flow rate) : 15~20kg COD/㎥day |
| Applicable Industry |
|
||
THIOPAQ (Biogas Desulfurization Equipment)
| Equipment |
THIOPAQ(Biogas Desulfurization Equipment) 
It is a system that removes hydrogen sulfide contained in biogas by combining a scrubber and a bioreactor. |
||
|---|---|---|---|
| Advantages |
|
||
| Applicable rang |
|
||
| Applicable Industry |
|
||
ANAMMOX
| Equipemt |
Nitrogen Wastewater Treatment Equipment(ANAMMOX) 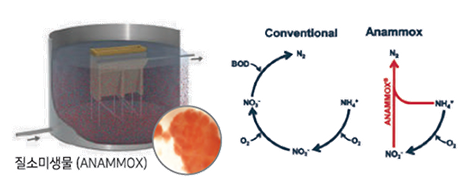
Unlike existing nitrification processes (NH4→NO2→NO3) and denitrification (NO3→N2), this is the technology that uses partial nitrification (NH4→NO2)process where granular ANAMMOX microorganism is removing nitrogen by using only the NH4and NO2 |
||
|---|---|---|---|
| Advantages |
|
||
| Applicable range |
|
||
Activated Sludge Process
A traditional biological treatment method that uses microorganisms to decompose pollutants and separates the sludge through a sedimentation tank.
MBR (Membrane Bioreactor)
An advanced treatment method that combines activated sludge and membrane separation to produce high-quality effluent.
SBR (Sequencing Batch Reactor)
A batch process in which all treatment stages are carried out sequentially within a single reactor.
A2O (Anaerobic-Anoxic-Oxic Process)
An advanced treatment method that removes nitrogen and phosphorus simultaneously through anaerobic, anoxic, and aerobic stages.
Overview
The water treated through the wastewater treatment system can be reused as industrial water, landscape irrigation water, process water, and more after passing through the reuse facilities.
By utilizing wastewater reuse facilities, it is possible to reduce wastewater generation and treatment costs, as well as achieve cost savings through decreased water consumption.


Process Flow
We deliver reliable and cost-efficient process designs tailored to the characteristics of wastewater and the specific quality requirements of our clients.
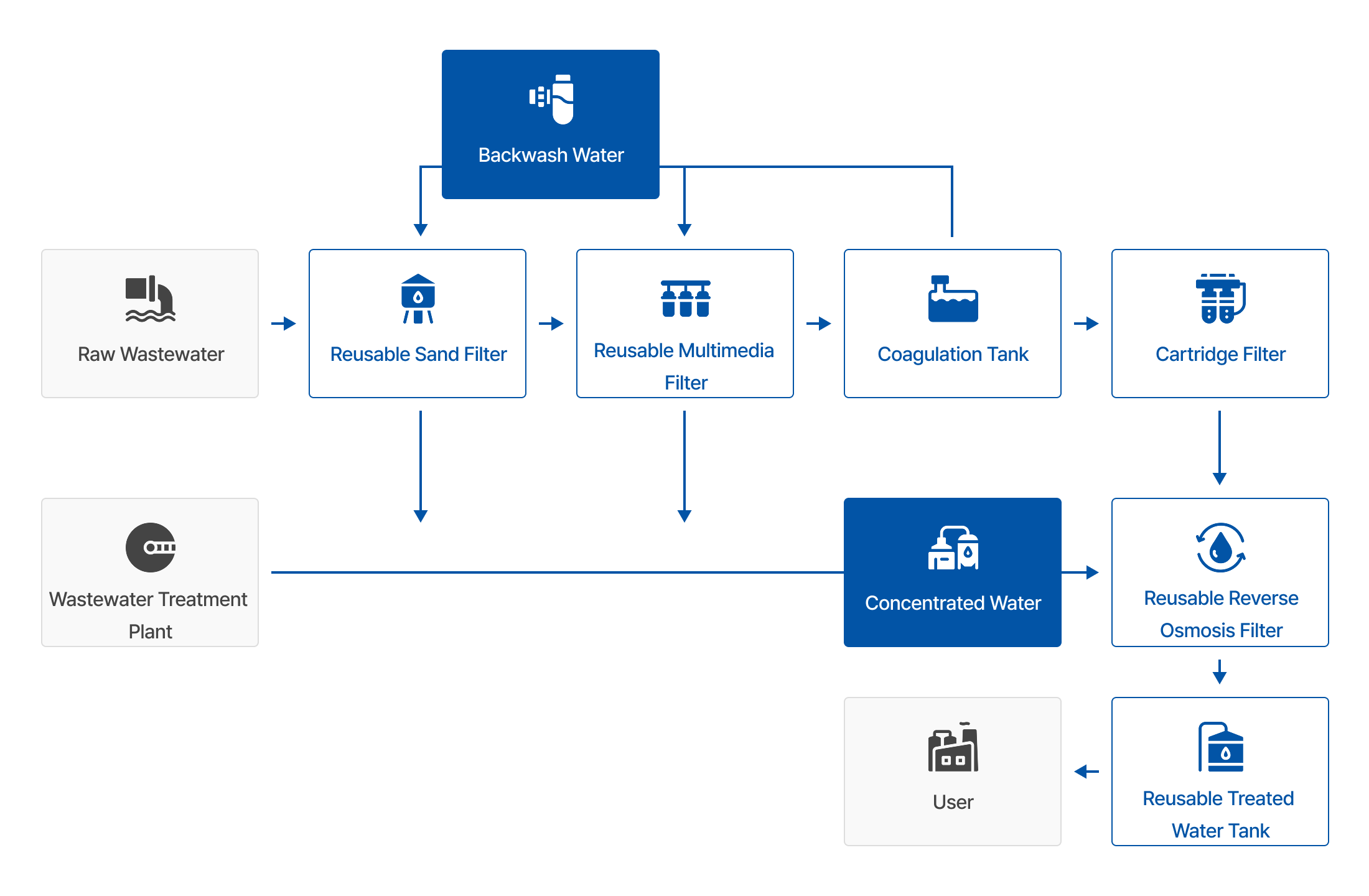
Equipment
Pre-treatment Equipment

: SAND filter, MMF, A/C filter, UF, etc.
- Removal of turbidity and suspended solids
- Removal of organic substances
RO System

: RO, UV sterilization, etc.
- Removal of turbidity, TDS, and TOC
- Removal of heavy metals and ions
- Removal of organics and sterilization
Multi–Disc Wastewater Sludge Dehydrator
| Equipment |
Multi–Disc Wastewater Sludge Dehydrator 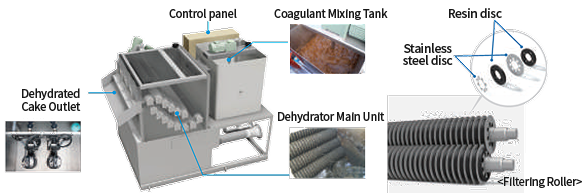
The coagulated sludge is compressed and dehydrated by each of filtering rollers |
||
|---|---|---|---|
| Advantages |
|
||
| Applicable range |
|
||

IWW Wastewater Treatment

High-Efficiency Anaerobic Reactor

High-Efficiency Anaerobic Reactor

High-Efficiency Anaerobic Reactor

High-Efficiency Anaerobic Reactor

High-Efficiency Anaerobic Reactor
 Swipe left or right to view the content.
Swipe left or right to view the content.| Project Name | Client | Facility | Capacity | Main Processes | Completion Year |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| New Wastewater Treatment Facility | POSCO E&C | Busan, Korea | Capacity: 375 ㎥/d, TN: 300 mg/L | Under Construction | ANAMMOX (Denitrification) |
| New Wastewater Treatment Facility | PT.TSPM | Indonesia |
High-conc.: 12 ㎥/d, CODcr: 130,000 mg/L Low-conc.: 50 ㎥/d, CODcr: 9,000 mg/L |
2024 | Evaporation (High-conc.) + MBR (Low-conc.) |
| Anaerobic Wastewater Treatment Installation & Expansion | NoodleLovers Inc. | Jincheon, Korea | 700 ㎥/d, CODcr: 3,500 mg/L | 2023 | ICX Reactor |
| Anaerobic Wastewater Treatment Installation & Expansion | NoodleLovers Inc. | Jincheon, Korea | 700 ㎥/d, CODcr: 3,500 mg/L | 2023 | MBR |
| New Wastewater Treatment Facility | Kolmar BNH | Sejong, Korea | 80 ㎥/d, CODcr: 1,000 mg/L | 2023 | Activated Sludge |
| New Wastewater Treatment Facility | Kolmar BNH | Sejong, Korea | 60 ㎥/d, CODcr: 25,000 mg/L | 2022 | Activated Sludge |
| Anaerobic Wastewater Treatment | Korea Paper | Siheung, Korea | 3,000 ㎥/d, CODcr: 7,000 mg/L | 2021 | IC Reactor |
| Anaerobic Wastewater Treatment | Asia Paper | Siheung, Korea | 10,000 ㎥/d, CODcr: 5,000 mg/L | 2021 | ICX Reactor |
| Biogas Desulfurization System | Samyang Corporation | Ulsan, Korea | 300Nm³/hr | 2021 | THIOPAQ (Desulfurization) |
| IWW Wastewater Treatment | UNIKEN | Ulsan, Korea |
High-conc.: 205 ㎥/d MBR: 261 ㎥/d |
2020 | Evaporation + MBR |
| High-Efficiency Anaerobic Reactor | Hite | Hongcheon, Korea | 3,000 ㎥/d, CODcr: 7,000 ppm | 2019 | IC Reactor |
| Anaerobic Wastewater Treatment (Plant 1) | Namyang F&B | Hongseong, Korea | 350 ㎥/d, CODcr: 5,000 ppm | 2019 | IC Reactor |
| Anaerobic Wastewater Expansion | Hanwha General Chemical Co., Ltd. | Ulsan, Korea | 3,800 ㎥/d, CODcr: 8,500 ppm | 2019 | UASB+ Reactor |
| Anaerobic Digester | OB Beer | Gwangju, Korea | 6,000 ㎥/d, CODcr: 4,000 ppm | 2018 | UASB Reactor |
| High-Efficiency Anaerobic Reactor | Haitai HTB | Cheonan, Korea | 2,000 ㎥/d, CODcr: 3,000 mg/L | 2017 | IC Reactor |
| High-Efficiency Anaerobic Reactor | Hankook Beverage | Namwon, Korea | 1,500 ㎥/d, CODcr: 1,500 mg/L | 2017 | IC Reactor |
| High-Efficiency Anaerobic Reactor | Samyang Corporation | Incheon, Korea | 3,000 ㎥/d, CODcr: 6,000 mg/L | 2015 | IC Reactor |
| High-Efficiency Anaerobic Reactor | Lotte Chilsung Beverage | Cheongju, Korea | 750 ㎥/d, CODcr: 2,200 mg/L | 2014 | IC Reactor |
| High-Efficiency Anaerobic Reactor | Samyang Corporation | Ulsan, Korea | 4,000 ㎥/d, CODcr: 5,000 mg/L | 2012 | IC Reactor |
| High-Efficiency Anaerobic Reactor | SEMPIO | Icheon, Korea | 500 ㎥/d, CODcr: 3,200 mg/L | 2011 | IC Reactor |
| High-Efficiency Anaerobic Reactor | Hite | Jeonju, Korea | 5,000 ㎥/d, CODcr: 11,000 mg/L | 2010 | IC Reactor |
| High-Efficiency Anaerobic Reactor | Lotte Chilsung Beverage | Opo, Korea | 2,500 ㎥/d, CODcr: 3,500 mg/L | 2008 | IC Reactor |
| High-Efficiency Anaerobic Reactor | Hansol Paper | Daejeon, Korea | 28,000 ㎥/d, CODcr: 20,000 mg/L | 2008 | IC Reactor |
| Wastewater Treatment Process Change & Expansion | Lotte Chilsung Beverage | Daejeon, Korea | 1,500 ㎥/d, CODcr: 4,000 mg/L | 2006 | IC Reactor |
| High-Efficiency Anaerobic Reactor | Daesang | Gunsan, Korea | 4,300 ㎥/d, CODcr: 4,400 mg/L | 2006 | IC Reactor |
| High-Efficiency Anaerobic Reactor | Lotte Samkang | Cheonan, Korea | 3,900 ㎥/d, CODcr: 5,000 mg/L | 2006 | IC Reactor |
| Anaerobic Wastewater Expansion | SINGSONG | Nonsan, Korea | 2,000 ㎥/d, CODcr: 9,600 mg/L | 2004 | IC Reactor |
| New Wastewater Treatment Facility | Kooksoondang | Hoengseong, Korea | 320 ㎥/d, CODcr: 2,700 mg/L | 2003 | IC Reactor |